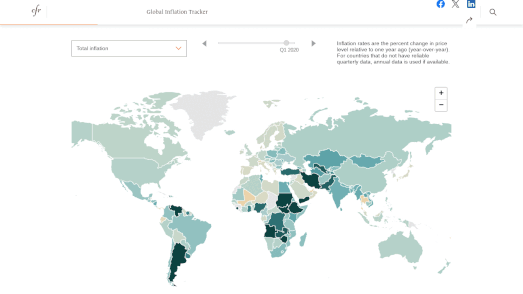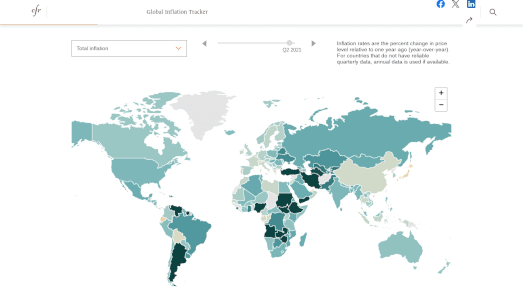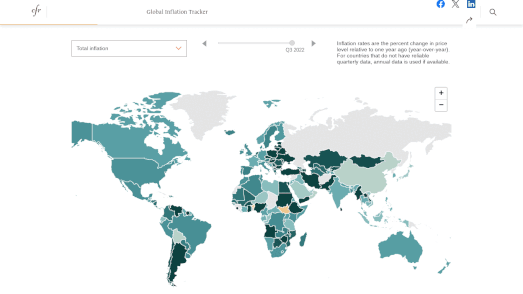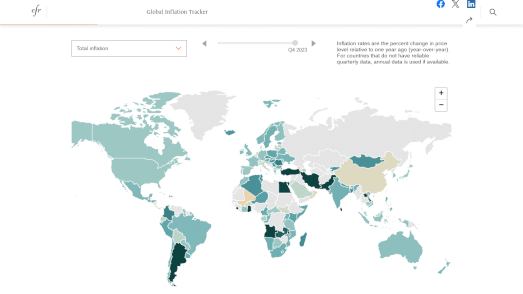
In the 1930s, under President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal, black homeowners across the United States were discriminated against through the creation of redlining maps. These maps identified areas with significant black populations and labeled them
as too high risk for mortgage support. Black homeowners living in these areas were therefore very unlikely to be successful when trying to refinance home mortgages from the government sponsored Home Owners' Loan Corporation.
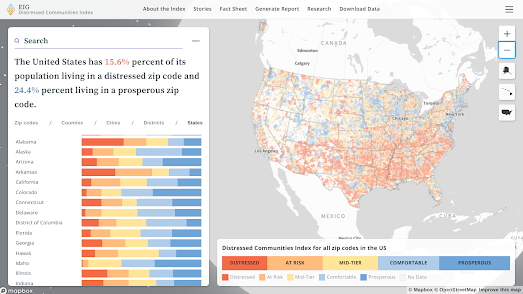
Unfortunately the racial discriminatory mortgage assessments of the 1930s have had a lasting legacy on American cities. A legacy which can still be felt in the United States today. Neighborhoods which were redlined as too high risk for mortgage lending in the 1930s have suffered from decades of under-investment in critical infrastructure. This historical under-investment means that anyone living in a once redlined neighborhood today is still likely to have less access to health care, be more at risk from extreme summer heat and is even at more risk of flooding than people living in neighborhoods which weren't redlined under Roosevelt's New Deal.
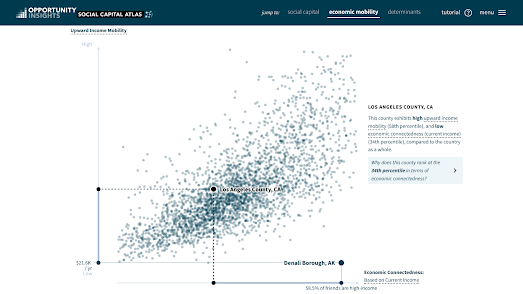
Flood Risk
One of the least obvious legacies of redlining is increased flood risk. It might not be immediately obvious that the denial of mortgage support in the 1930's would lead to a higher risk of flooding. However Bloomberg has released a convincing story map which shows that redlined neighborhoods in the U.S. have a much higher flood risk than their more affluent neighbors.
Bloomberg's Redlined, Now Flooding compares historical redlining maps with modern flood risk maps. This comparison reveals that in cities across the United States there is a greater risk of flooding in formerly redlined neighborhoods than in more affluent neighborhoods in the same city.
The reason why redlined neighborhoods have a higher flood is a direct result of "disparities in development compounded by decades of disinvestment". Since the 1930's more affluent neighborhoods have received greater investment in essential infrastructure compared to less affluent redlined neighborhoods. The result is that redlined neighborhoods are now at greater risk of flooding. And not just flooding ...
Urban Heat Islands
Redlined neighborhoods don't just face a greater risk of flooding. Since the New Deal's racially discriminated mortgage lending assessments of American cities redlined neighborhoods have continued to face under investment in infrastructure compared to the more wealthy greenlined neighborhoods.
For example, last year the New York Times mapped out how racist housing segregation, dating back to the Home Owners' Loan Corporation's Redlining maps, is a major contributory factor to the location of urban heat islands in modern towns and cities across the United States. In How Decades of Racist Housing Policy Left Neighborhoods Sweltering the NYT uses a story map to show how across the United States neighborhoods which were redlined are now usually the hottest parts of towns and neighborhoods which weren't redlined tend to be the coolest.
The reason for this is that redlined neighborhoods have largely remained areas of deprivation and tend to have fewer trees and a denser built environment than more affluent neighborhoods. Non-redlined neighborhoods are more likely to have lots of parks, grass and far more trees. All factors which help to deter the build-up of urban heat.
Health Inequality
The legacy of the Home Owners' Loan Corporation (HOLC) redlining maps can also still be seen in the health inequality in cities today. The Digital Scholarship Lab and the National Community Reinvestment Coalition has used maps to show how redlined neighborhoods suffer severe health disparities in the 21st Century compared to more wealthy neighborhoods.
Not Even Past: Social Vulnerability and the Legacy of Redlining allows you to directly compare redlining maps with modern maps which
visualize the modern health disparities in U.S. cities. Select a city on the Not Even Past website and you can view its HOLC redlining map placed side-by-side with a map which shows the CDC's current Social Vulnerability Index scores for the city's neighborhoods. This allows you to make a direct comparison between the two maps and see where the health disparities in your city today are a partial legacy of historical redlining.
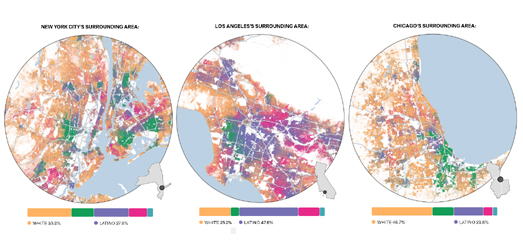
Racial Segregation
One of the biggest lasting legacies of redlining has been the continuing racial segregation seen in many American cities. Wenfei Xu's Redlining Map
visualization allows you to explore for yourself if the HOLC redlining maps have had a lasting impact on segregation in your city. Using modern census data alongside the HOLC redlining maps you can see which neighborhoods have a high percentage of black, white or Hispanic people and see if these areas correlate with areas which were deemed at risk or safe for lending purposes in the 1930's.
You probably won't be surprised to discover that black Americans are far more likely to live in neighborhoods which were redlined 90 years ago. The result of the continuing disinvestment of America's once redlined neighborhoods is that many black Americans today live in the neighborhoods which have the lowest average incomes, the poorest access to health services, the worst urban heat islands and are at greater risk of flooding.