The Disastrous Growth of Arctic Wildfires
Temperatures in some parts of the Arctic this year have risen as much as 30C. Because of global heating the Polar Jet Stream is slowing down, which in turn can lead to extended punishing heat waves in the Arctic. Another effect of global heating is an increase in lightning strikes in the Arctic.
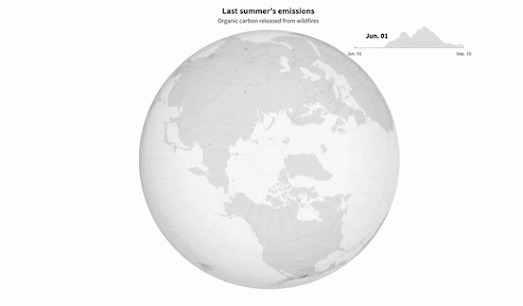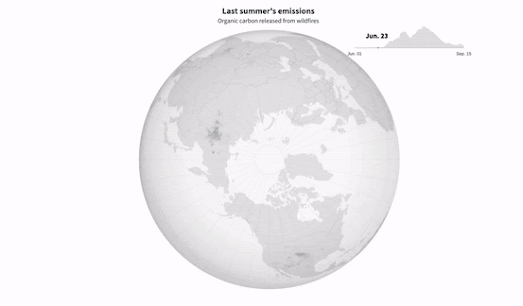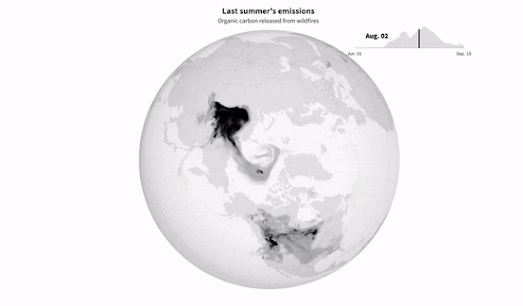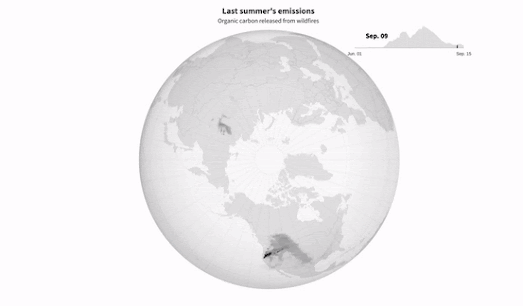
This combination of extreme high temperatures, slower air circulation, and increased lightning strikes means that wildfires are shifting further north and are beginning to increasingly blaze through boreal forest and tundra - releasing huge amounts of greenhouses gases from an area blessed with carbon rich soil.In Why Arctic Fires are Releasing More Carbon Than Ever Reuters has mapped out the organic compounds released by wildfires in the Arctic between June 1st and September 15th 2021. Last year Artic wildfires caused the release of over 16 million tonnes of carbon. On average Arctic wildfires release around 15% of the world’s annual carbon emissions from fires. That percentage is now rapidly increasing due to the combination of the growing number of wildfires in the Arctic and the area's carbon rich soil.
Last year the Arctic accounted for nearly 33% of the total global carbon emissions from fire.


Comments