The History of Machine Learning & Street View

MIT is using machine learning & Google Maps Street View to automatically detect which areas of a city are evolving faster than other neighborhoods in the same city. Google Maps now includes historical Street View imagery for a number of cities around the world. MIT is able to compare this historical imagery to the most recent Street View imagery of the same location to 'quantify urban change'. MIT's Streetchange project has so far assessed 1.5 million blocks in five different American cities.
This isn't the first time that MIT has used Google Street View imagery and machine learning to carry out remote analysis of the urban environment. MIT's Place Pulse project is a crowd-sourced experiment using Street View to rate the perceived safety of city streets. The project aims to quantitatively recognize which areas of a city are perceived as wealthy, modern, safe, lively, active, unique, central, adaptable or family-friendly based on how people respond to Street View images of the city.
From this project MIT then took the crowd-sourced safety rankings for 3,000 street images from New York and Boston to create an algorithm to automatically score city streets for safety based on their Street View images. Using the Place Pulse scores MIT assigned attributes to features present in the images, associated with the image's textures, colors and shapes. They then used machine learning to associate image features with scores of perceived safety. MIT can then use the resulting algorithm to predict the perceived safety of a new image. They can therefore give any Street View image a 'StreetScore' based on the results of the Place Pulse survey.
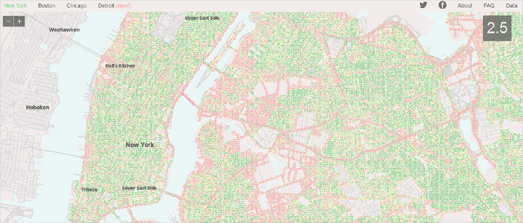
StreetScore includes a number of maps showing areas of perceived safety in New York, Boston, Chicago and Detroit. Using Street View images of the city StreetScore assesses the perceived safety of locations throughout the city. Green dots on the map represent the areas which StreetScore has assigned as having a high perceived safety rating and the red dots are the locations with a low perceived rating score.
MIT's new Streetchange project has compared historic Street View imagery of Baltimore, Boston, Detroit, New York and Washington DC with the most recent Google Street View imagery from the same locations.
The Streetchange maps of each city rate each census tract in the city by the amount of urban change found in the district. Each city map also shows individual locations with high Streetchange rankings with white map markers. If you mouse-over these individual markers you can actually compare the historic and most recent Street View images for yourself to see how much the location has changed.
The Streetchange website has more information about how they have used computer vision to assess changes in the urban environment.This includes individual examples from the featured cities. You can also read the team's academic paper (PDF) to learn more.


Comments